If you are new to Internet of things,I strongly suggest going through Introduction to Internet of Things to get basics right.Also,you can check out other blogs at Tech-a-techblog .
So we discussed in the blog Components of IOT,that IOT consists of Things,Sensors and Actuators,People,Communication protocols,Cloud and Analytics.So,in this blog post we’ll discuss about different Communication protocols used in IOT.
There are two types of Communication Protocols:
•Wireless Communication
•Wired Communication
Today,we’ll discuss about wired communication.
The wired communication is divided into two categories:
Internal Communication:
1. I2C
2. SPI
External Communication
1. Ethernet
2. RS-232
3. RS-485
4. UART
5. USART
6. USB
We’ll discuss them one by one starting with:
Internal Communication
1) I2C :
I2C stands for “Inter-integrated circuit” bus.It was developed for television by Philips Semiconductor, 1980 • In I2C devices processors, EEPROMs, sensors, real-time clocks are used as a control interface and I2C devices can also have separate data interface (digital TV tuners, video decoders, audio processors …).There are 3 types of I2C based on speed : Slow (under 100 Kbps) ,Fast (400 Kbps) ,High-speed (3.4 Mbps).
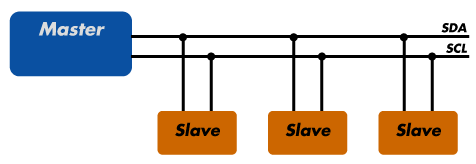
As you can see in image above there are two wire lines i.e Serial Data(SDA) and Serial Clock(SCL).Several slave devices can be connected to a master device using I2C.
Advantages and Disadvantages of I2C:
Advantages :
•Useful for devices that communicate occasionally
•Addressing scheme allows multiple device
•Interconnection without additional wires.
Disadvantages :
•Hardware and especially software implementation more complicated than the SPI Half-duplex.
•Not scalable for large number of devices.
2) SPI :
The Serial Peripheral Interface bus (SPI) is a synchronous serial communication interface specification used for short distance communication, primarily in embedded systems. The interface was developed by Motorola in the late 1980s. Typical applications include Secure Digital cards and liquid crystal displays.
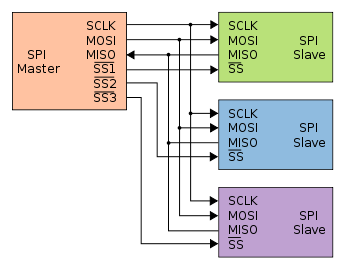
As you can see in the image above that slave devices have 4 connections i.e SCLK(Serial Clock) ,MOSI(Master Output Slave Input) ,MISO(Master Input Slave Output) ,SS(Slave Select).First 3 pins share same line from controller but SS pin controls which slave device is active.
Advantages and Disadvantages of SPI:
Advantages :
•It’s faster than asynchronous serial
•The receive hardware can be a simple shift register
•It supports multiple slaves
Disadvantages :
•It requires more signal lines (wires) than other communications methods
•The communications must be well-defined in advance.
•The master must control all communications (slaves can’t talk directly to each other)
•It usually requires separate SS lines to each slave, which can be problematic if numerous slaves are needed.
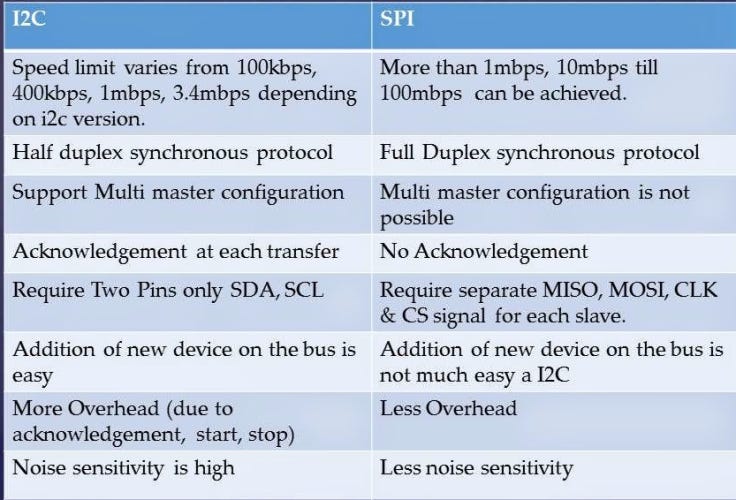
Below Image compares the two Internal wired communication methods.
External Communication
1)Ethernet :
A system for connecting a number of computer systems to form a local area network, with protocols to control the passing of information and to avoid simultaneous transmission by two or more systems.The first widely used LAN technology was developed in the mid-1970s by researchers at the Xerox Palo Alto Research Centers (PARC).Its simpler and cheaper than token LANs and ATM. Every Ethernet network interface card (NIC) is given a unique identifier called a MAC address. The MAC address comprises of a 48-bit number. Within the number the first 24 bits identify the manufacturer and it is known as the manufacturer ID or Organizational Unique Identifier (OUI) and this is assigned by the registration authority.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Ethernet:
Advantages :
•Network start with it and end with it.
•Reliable and can be used within a building , doesn’t matter how many floor.
•It will be needed switch to keep network.
•It is basically used for making LAN.
Disadvantages :
•Can’t be used for long distance network. copper or Fiber will help here.
•In a building network , you have to connect Ethernet to switch and then Ethernet again which makes such network, a hell (with presence of lot of cables)which is very irritating and tough to manage.
Application of Ethernet :
•Cloud Computing
•Site to Site Access
•Video Applications
•Distributed Storage Area Networks
•CCTV
•Copper cable
•Fiber optic cable
2)RS-232 :
RS-232 stands for Recommended Standard 232.It is basically a interface standard.It is commonly used in computer serial ports.The standard defines the electrical characteristics and timing of signals.The current version of the standard is TIA-232-F ,issued in 1997.
Advantages and Disadvantages of RS-232:
Advantages :
•Simple wiring and connectors
•Widely available
•Low cost
•Most embedded processor include this interface
•Software to implement a serial port is easy
Disadvantages :
•Not as commonly used
•Less standardized connectors and terminology
•Half-duplex master-slave operation
Application of RS-232 :
•Serializes data to be sent to modem
•De-serializes data received from modem
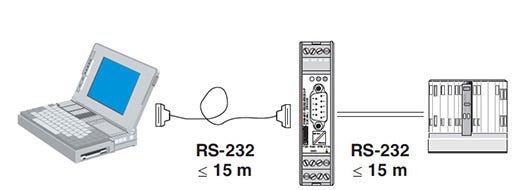
3)RS-485 :
RS-485 (EIA-485 Standard) is an improvement.It increases the number of devices from 10 to 32 and defines the electrical characteristics necessary to ensure adequate signal voltages under maximum load.It can create networks of devices connected to a single RS- 485 serial port.The noise immunity and multi-drop capability make RS-485 the serial connection of choice in industrial applications.RS-485 hardware may be used for serial communication with up to 4000 feet of cable.
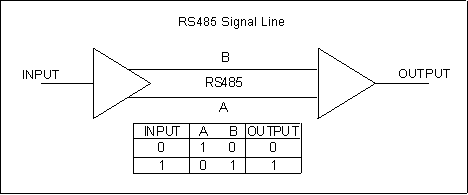
Advantages and Disadvantages of RS-485:
Advantages :
•Low cost
•Immune to noise
•Multipoint applications
•Operates on a single pair of wires
Disadvantages :
•Not as commonly used
•Less standardized connectors and terminology
•Half-duplex master-slave operation
Application of RS-485 :
•RS-485 signals are used in a wide range of computer and automation systems.
•RS-485 is used as the physical layer underlying many standard and proprietary automation protocols used to implement Industrial Control Systems
•RS-485 is also used in building automation as the simple bus wiring and long cable length.
•It is also used in model railway.
4)UART :
UART is the name for the hardware used for a RS-232 Serial Interface.UART stands for Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter.Early PCs had a UART chip, but this functionality is now found inside a larger chip that also contains other I/O features.A UART may be used when high speed is not required or an inexpensive communication link between two devices is required . UART communication is very cheap.Asynchronous because no clock signal is transmitted.
UART adds start and stop bits to the data packet being transferred. These bits define the beginning and end of the data packet so the receiving UART knows when to start reading the bits.When the receiving UART detects a start bit, it starts to read the incoming bits at a specific frequency known as the baud rate. Baud rate is a measure of the speed of data transfer, expressed in bits per second (bps).
Advantages and Disadvantages of UART:
Advantages :
•Single wire.
•Easy interface to PCs.
•Range of standard physical interfaces (TTL, RS232, RS422, RS485).
Disadvantages :
•Needs reasonable clock accuracy both ends.
•Max data rate in practice about 1mbit/sec (typically limited by UART capabilities).
Application of UART :
•Transmitting and receiving UARTs must be set for the same bit speed, character length, parity, and stop bits for proper operation.
•Very low-cost home computers or embedded systems dispense with a UART and use the CPU to sample the state of an input port or directly manipulate an output port for data transmission.
•Typical serial ports used with personal computers connected to modems use eight data bits.
5)USART :
The USART module is a full duplex, serial I/O communication peripheral.It contains all shift registers, clock generators and data buffers needed for serial communication.It can work in synchronous mode, or in asynchronous mode.The USART uses two I/O pins to transmit and receive serial data. Both transmission and reception can occur at the same time i.e. ‘full duplex’ operation.
Asynchronous Mode:
•Data transfer happens in the following way:
•In idle state, data line has logic high (1).
•Data transfer starts with a start bit, which is always a zero.
•Data word is transferred (8 or 9 bit), LSB is sent first.
•Each word ends with a stop bit, which is always high (1).
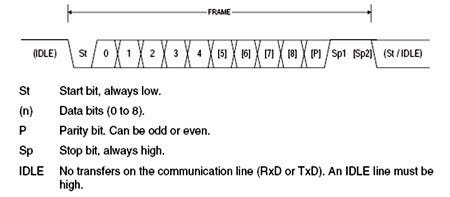
6)USB :
It is a representative peripheral interface.USB stands for Universal Serial Bus.It provides a serial bus standard for connecting devices,usually to a computer, but it also is in use on other devices such as set-top boxes, game consoles and PDAs.

USB Standard :
•USB 1.0 specification introduced in 1994
•USB 2.0 specification finalized in 2001 : Became popular due to cost/benefit advantage.
•E.g. IEEE 1394 — high bandwidth, high cost
•Three generations of USB : USB 1.0 , USB 2.0 , USB 3.0
Advantages and Disadvantages of USB :
Advantages :
•Flash drives use little power, have no fragile moving parts, and for most capacities are small and light.
•Data stored on flash drives is impervious to mechanical shock, magnetic fields, scratches and dust.
Disadvantages :
•Flash drives can sustain only a limited number of write and erase cycles before the drive fails.
•A drawback to the small size is that they are easily misplaced, left behind, or otherwise lost.
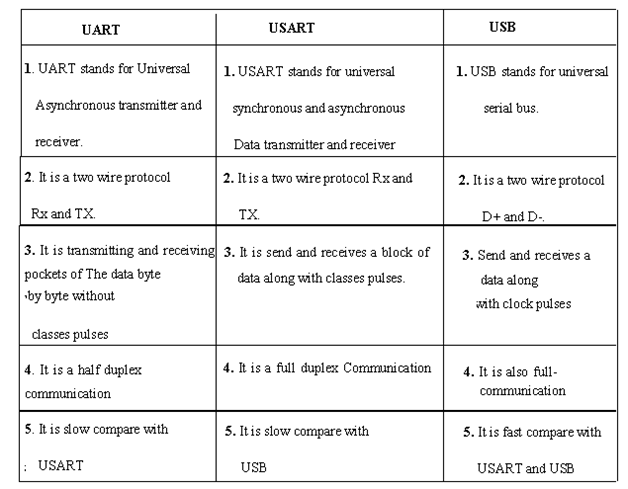
Below Image differentiates between UART,USART and USB.
If you want to learn about wireless Communication Protocols in IOT, you can refer to Wireless Communication Protocols.
Leave your Queries in comments below,i would be happy to answer them.
See ya!!